Category List
Featured List


Master RSI: Effective Methods to Spot Divergence and Convergence
The Relative Strength Index (RSI) is more than just a popular indicator among crypto traders; it's a powerful tool revered for its mathematical foundation and versatility. This guide will delve into advanced techniques using the RSI, focusing on how to effectively spot and trade divergence and convergence signals
Unlike some indicators that rely on complex calculations, the RSI achieves a remarkable balance between mathematical sophistication and ease of interpretation. This makes it accessible to both novice and experienced traders, while still providing the depth needed for advanced trading strategies
In the following sections, we will explore popular techniques using RSI for convergence and divergence signals.
Relative Strength: Understanding RSI Calculation
At the heart of the RSI lies the concept of Relative Strength (RS), which measures the magnitude of recent price changes to evaluate overbought or oversold conditions in the price of a cryptocurrency or other asset. Let's break down the calculation to understand how it works.
The relative strength of the price changes of cryptocurrencies gives insights into what could be going on in the market and what to expect for the consequent movements. If the 'RS' is stepping upward, it might indicate a reliable uptrend momentum to follow. Otherwise, stepping downward could be considered a downtrend.
Traditionally, an RSI reading above 70 suggests that an asset is becoming overbought and may be primed for a trend reversal or corrective pullback. Conversely, an RSI reading below 30 indicates an oversold or undervalued condition.
For a deep understanding of the RSI calculation and its role, let's break down the formula:
- Average gain calculation: Results from averaging the price increment during a period, typically 14 days, but adjustable for traders' goals.
- Average loss calculation: Results from averaging the price decrease during the same period, in absolute terms.
- Relative Strength (RS): The RS comes from dividing the average gain by the average loss.
The Formula
To generate values between 0 - 100, the RSI uses the Relative Strength in the following calculation:
- RSI = 100 - (100 / (1+RS))
- RS = Average Gain of determined number of periods (UP) / Average Loss of determined number of periods (DOWN)
How RSI Periods Impact the Indicator’s Performance?
Although the standard period for the RSI is usually 14 days, it is adjustable to meet specific strategies. Altering this value causes the RSI to reach overbought and oversold levels faster or slower according to current changes in market prices.
For instance:
- Values below 14 increase the indicator’s sensitivity, so it responds quickly to price changes.
- Conversely, values above 14 decrease the response of the indicator, making it act slowly.

| Divergence: A market situation where the price direction of an asset differs from the direction or signal of a technical indicator, often suggesting a potential trend reversal. |
Common RSI Divergence/Convergence Strategies
Traders have been using the RSI primarily to identify divergence and convergence between the price and the indicator or against other indicators.
Using the RSI to look for divergence and convergence helps traders gauge weakening momentum and take advantage of potential reversal points in the price action.
Let's illustrate some RSI divergence and convergence scenarios that typically emerge in markets.
Bullish Divergence
This occurs when the price of an asset makes a lower low while the RSI forms a higher low. This discrepancy suggests that the downward momentum is weakening, and a potential bullish reversal might be imminent.

To confirm a bullish divergence, traders often look for additional signals, such as:
- Bullish Candlestick Patterns: A hammer, bullish engulfing, or morning star pattern forming near the second low.
- Support Level Bounce: The price bouncing off a key support level, indicating buying pressure.
- Trendline/Channel Break: A break above a descending trendline or channel connecting the two lows in the price chart.
- Other Indicators: Confirmation from other indicators like MACD (bullish crossover) or an increase in On-Balance Volume (OBV).

Bearish Divergence
For the bearish case, the price makes a higher high while the RSI forms a lower high. The bearish divergence indicates that an uptrend momentum is weakening, and the likelihood of a downward price reversal is increasing.

To confirm a bearish divergence, traders often look for additional signals, such as:
- Bearish Candlestick Patterns: Downward engulfing candlestick or shooting star patterns forming near the higher high.
- Resistance Levels: The price struggling around a key resistance level, indicating selling pressure.
- Trendline/Channel Break: A break below an ascending trendline or channel joining the two highs in the price chart.
- Other Indicators: Confirmation from other indicators like Stochastic Oscillator when identifying an overbought/oversold condition, divergence, and bearish crossover.

Example of Stochastic Oscillator signals.
Bullish Convergence
This occurs during an uptrend when the price makes a higher low, but the RSI makes a lower low. This indicates that the underlying bullish momentum is still strong, and the uptrend is likely to continue after a minor pullback.

Confirm bullish convergence with signals like:
- Volume: An increase in volume as the price makes a higher low supports the bullish signal.
- Candlestick Patterns: Bullish patterns forming near the higher low.
- Moving Average: Price holding above a key moving average (e.g., 50-period).
- Other Indicators: MACD histogram rising, or Stochastic forming a higher low.

Bearish Convergence
For the bearish convergence, during a downtrend the price makes lower lows and lower highs while RSI forms higher highs. This condition indicates strength in the downward momentum, and increases the chances of a continuation of the price decline.
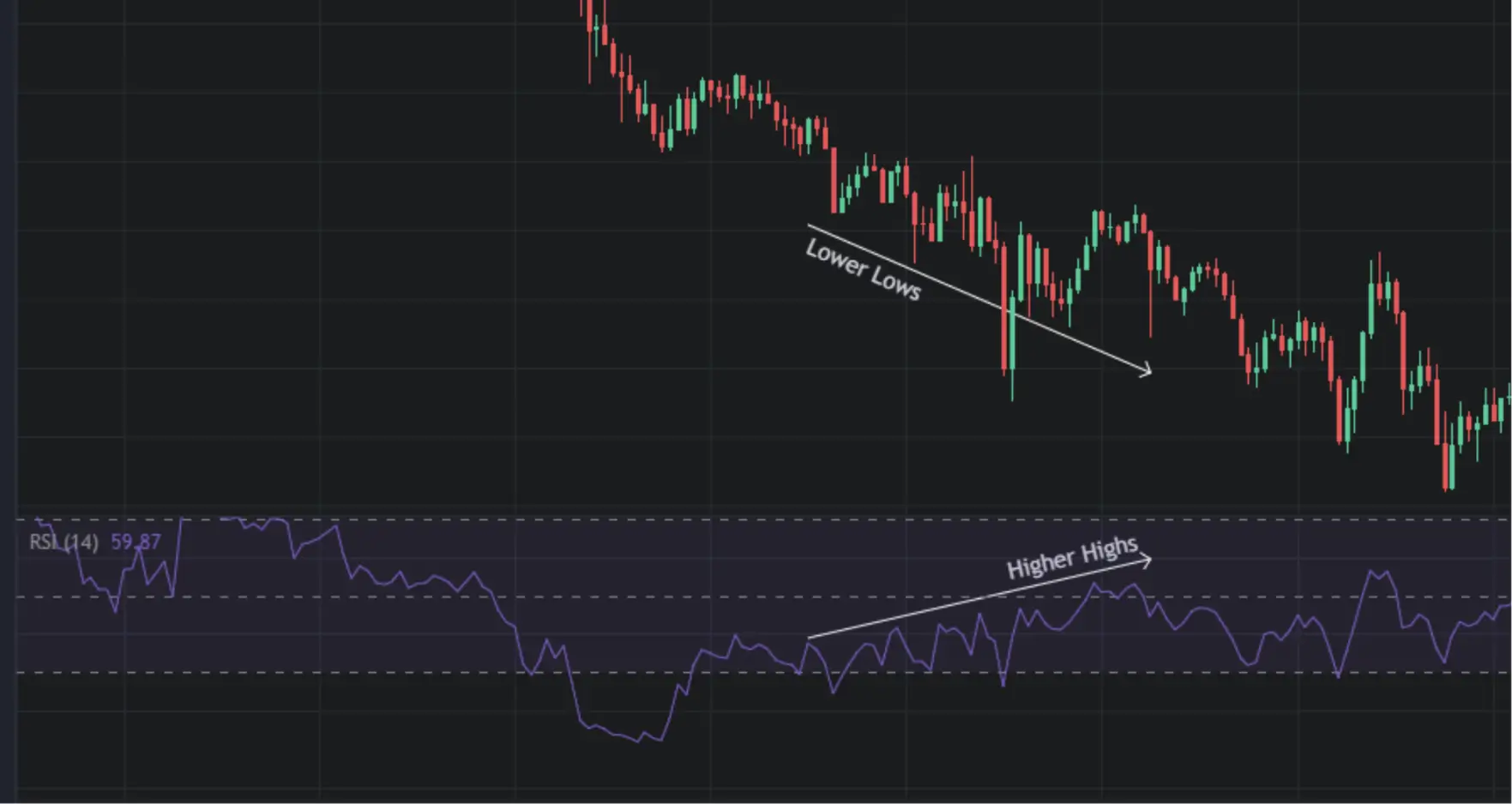
Confirm bearish convergence with signals like:
- Volume: An increase in volume as the price makes a lower lows supports the bearish trend.
- Candlestick Patterns: Bearish patterns forming near the lower high.
- Moving Average: Price holding below a key moving average (e.g., 50-period).

| Confluence: It refers to a scenario where multiple indicators (technical, fundamental or price action) point out the same potential outcome for an upcoming market move. For example, a support level coinciding with an oversold condition in the RSI can be considered confluence |
Advanced Techniques for RSI Divergence/Convergence
To enhance the reliability of divergence and convergence signals, consider these advanced techniques:
- Confluence with Support/Resistance: Look for divergence or convergence signals that occur near key support or resistance levels. This confluence of signals increases the probability of a successful trade.
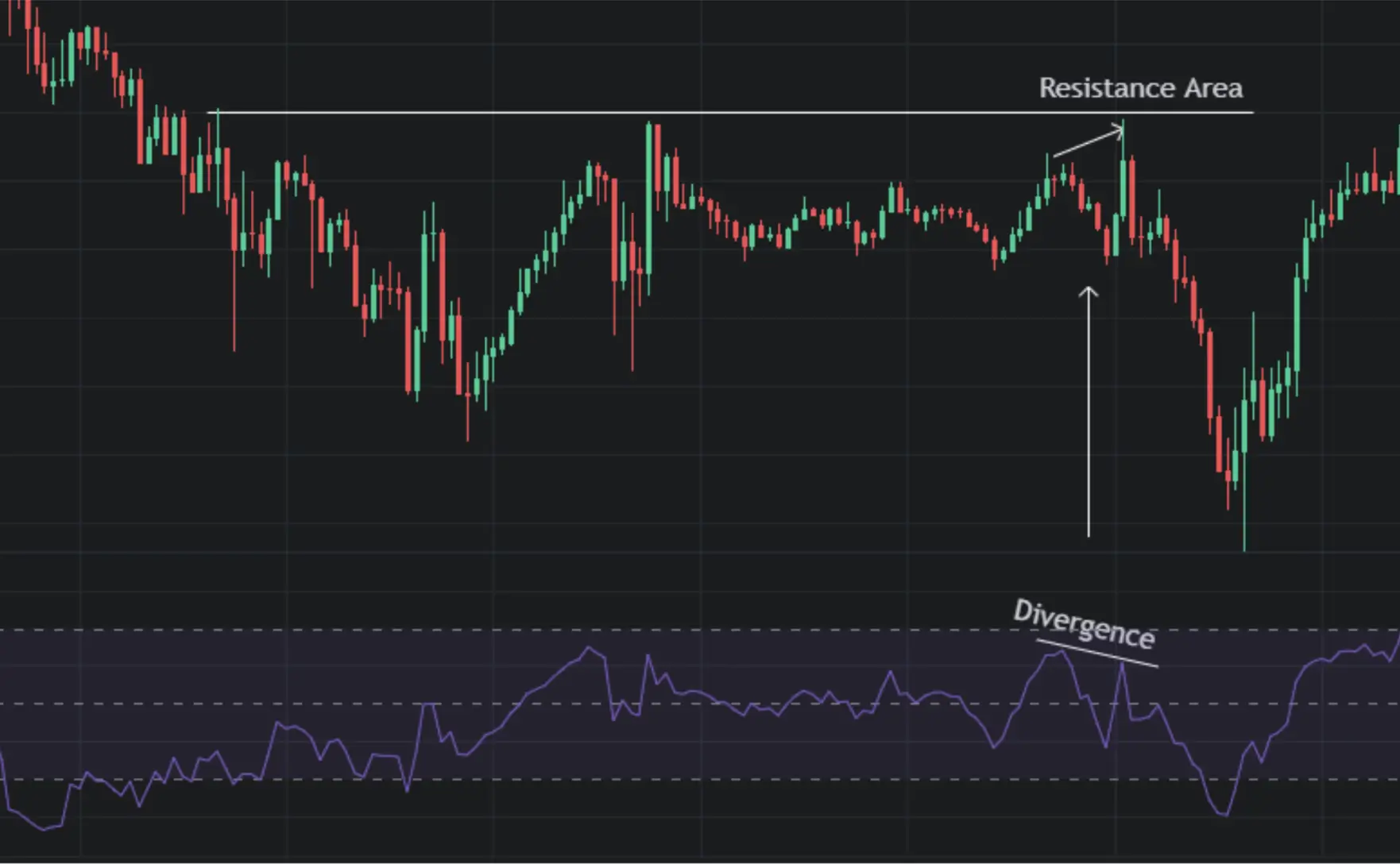
1-hour Chart
- Multiple Timeframe Analysis: Analyze divergence/convergence on multiple timeframes. For instance, you might identify a bearish divergence (as shown above) on the 1-hour chart and then look for confirmation on the 30-min chart before entering a short position.

30-min Chart
- Combining with Chart Patterns: Identify chart patterns (e.g., double bottoms, head and shoulders, triangles) that are accompanied by RSI divergence or convergence. This combination can provide powerful trading signals.
Combining RSI with other indicators can filter out false signals and provide stronger confirmation. Some effective combinations include:
- RSI + MACD: Look for MACD crossovers that confirm RSI divergence or convergence. For example, a bullish MACD crossover occurring at the same time as a bullish RSI divergence strengthens the reversal signal.

- RSI + Bollinger Bands: Use RSI divergence or convergence near the upper or lower Bollinger Bands to identify potential reversals. For instance, a bearish divergence on the RSI when the price is near the upper Bollinger Bands could signal an impending pullback.

- RSI + Stochastic Oscillator: Combine RSI and Stochastic to confirm overbought/oversold conditions and divergence/convergence signals. For example, if both RSI and Stochastic show bearish divergence, it adds weight to the bearish signal.

For this guide, let's discuss more interesting approaches regarding divergence and convergence signals, like using volume and discovering hidden divergences.
| MACD: It stands for Moving Average Convergence Divergence, which is an oscillator designed to gauge market momentum by assessing the relationship between two moving averages while displaying a histogram. |
RSI with Volume indicator
Analyzing volume alongside RSI can provide valuable insights into the strength and validity of divergence and convergence signals. Here's how to use them together.
- Confirmation of Breakouts: When the RSI breaks above 70 (overbought) or below 30 (oversold) accompanied by a surge in volume, it suggests strong momentum behind the move. This can be a powerful confirmation signal, especially when combined with divergence. For example, if you see bullish divergence on the RSI and then the price breaks above a resistance level with high volume and the RSI moving out of oversold territory, it strengthens the bullish signal.
- Divergence/Convergence Confirmation: Ideally, you want to see volume confirming the divergence or convergence. For example, in a bullish divergence, you would ideally see increasing volume as the RSI makes a higher low, suggesting growing buying pressure. In a bearish divergence, you would look for increasing volume as the RSI makes a lower high, indicating increasing selling pressure. If the volume is low or decreasing during a divergence/convergence, it could be a warning sign of a potential false signal.
- Volume on Breakouts: When the price breaks a key support or resistance level, look for confirmation from both the RSI and volume. A breakout accompanied by high volume and a corresponding move in the RSI (e.g., breaking above 70 in an uptrend or below 30 in a downtrend) suggests strong momentum and a higher probability of a sustained move.
Hidden Divergence
Hidden divergence is a powerful continuation pattern that often signals a resumption of the prevailing trend. Unlike regular divergence, which hints at reversals, hidden divergence suggests that the current trend is likely to persist.
Types of Hidden Divergence:
- Bullish Hidden Divergence: Occurs in an uptrend. The price makes a higher low, but the RSI makes a lower low. This indicates that despite the price pullback, the underlying momentum remains bullish.
- Bearish Hidden Divergence: Occurs in a downtrend. The price makes a lower high, but the RSI makes a higher high. This suggests that despite the price bounce, the underlying momentum remains bearish.
Trading Hidden Divergence:
- Identify the Trend: Confirm the existing trend direction on a higher timeframe (e.g., daily or 4-hour).
- Spot the Divergence: Look for instances where the price makes a higher low (in an uptrend) or a lower high (in a downtrend) while the RSI makes a lower low or a higher high, respectively.
- Confirmation: Seek additional confirmation from other indicators (e.g., MACD, trendlines, moving averages) or candlestick patterns before entering a trade.
- Entry: For bullish hidden divergence, consider entering a long position after a bullish confirmation signal (e.g., a bullish engulfing pattern or a break above a short-term resistance level). For bearish hidden divergence, consider entering a short position after a bearish confirmation signal.
- Stop-Loss: Place your stop-loss below the recent swing low in a bullish setup or above the recent swing high in a bearish setup.
- Take-Profit: Set your take-profit target based on the next significant resistance level in an uptrend or support level in a downtrend.
Risk Management Considerations to Avoid Typical Pitfalls
Some mistakes when using RSI may come from wrong interpretations and taking false signals. To avoid such pitfalls, it is a good practice to carry with a set of rules regarding opening trades and protecting them properly.
Effective risk management is crucial when trading RSI divergence and convergence. To avoid common pitfalls and protect your capital, consider these guidelines:
- Always Use Stop-Losses: Place stop-loss orders below the recent swing low for bullish setups and above the recent swing high for bearish setups. This limits potential losses if the trade moves against you.
- Proper Position Sizing: Determine your position size based on your risk tolerance and account size. The 1% rule (risking no more than 1% of your account on any single trade) is a widely used guideline.
- Wait for Confirmation: Don't jump into a trade based solely on divergence or convergence. Wait for confirmation signals from other indicators, candlestick patterns, or price action before entering.
- Avoid Overtrading: Divergence and convergence signals are not always accurate. Don't chase every signal you see. Focus on high-probability setups that meet your criteria.
- Be Aware of False Signals: RSI, like any other indicator, can generate false signals. Be prepared for the possibility of losing trades and factor this into your risk management plan.
Lets use a table to illustrate an example of rules for risk management using RSI for the divergence and convergence strategy.
| Entry Condition | RSI Signal | Price Action | Managing Risk |
|---|---|---|---|
Bullish Divergence | RSI line indicates a higher low WHILE price makes a lower low | Price is heading to support level. | Evaluate an entry after a bullish candlestick pattern. Set a stop-loss order below the bullish candlestick. |
Bearish Convergence | RSI line falling with price | Market is in a downtrend. | Evaluate a short position after a trend confirmation. For example: low volume during a retracement while RSI moves notably for the downside and a bearish candlestick appears. |
Conclusion and Call to Action
The Relative Strength Index (RSI) is a powerful tool for identifying potential trend reversals and continuations through divergence and convergence signals.
By mastering these techniques and combining them with other forms of analysis, you can significantly enhance your trading decisions in the cryptocurrency market.
Ready to take your RSI trading to the next level? Sign up for a free trial of Altrady and explore their advanced charting tools.
Practice spotting divergence and convergence, set up custom RSI alerts, and use their paper trading feature to test your strategies risk-free.
Altrady provides the platform you need to effectively implement RSI in your trading plan. Start mastering RSI divergence and convergence today!





























